

Polymorphism java example shape of objects code#
Now, if we extend this class to create a Rectangle class (the area formula is quite different from a triangle had we created a class called Triangle), we need to write only the Rectangle class and part of the code that instantiates the Rectangle object. Other derived implementation may be used as it is implemented by the superclass without making any changes.įor example, a Shape class contains a method called area(). As per the norms of inheritance, a new class acquires the property and methods of the superclass and is open to override only those methods that it is interested in modifying. The new class becomes part of the classification, like a Lego attached to a construction in such a manner that the construction would not crumble even if we detach one. That means we can assign new classes with almost no modification of the existing code, provided the class is part of the inheritance hierarchy. Polymorphism in Java Leverages Extensibility
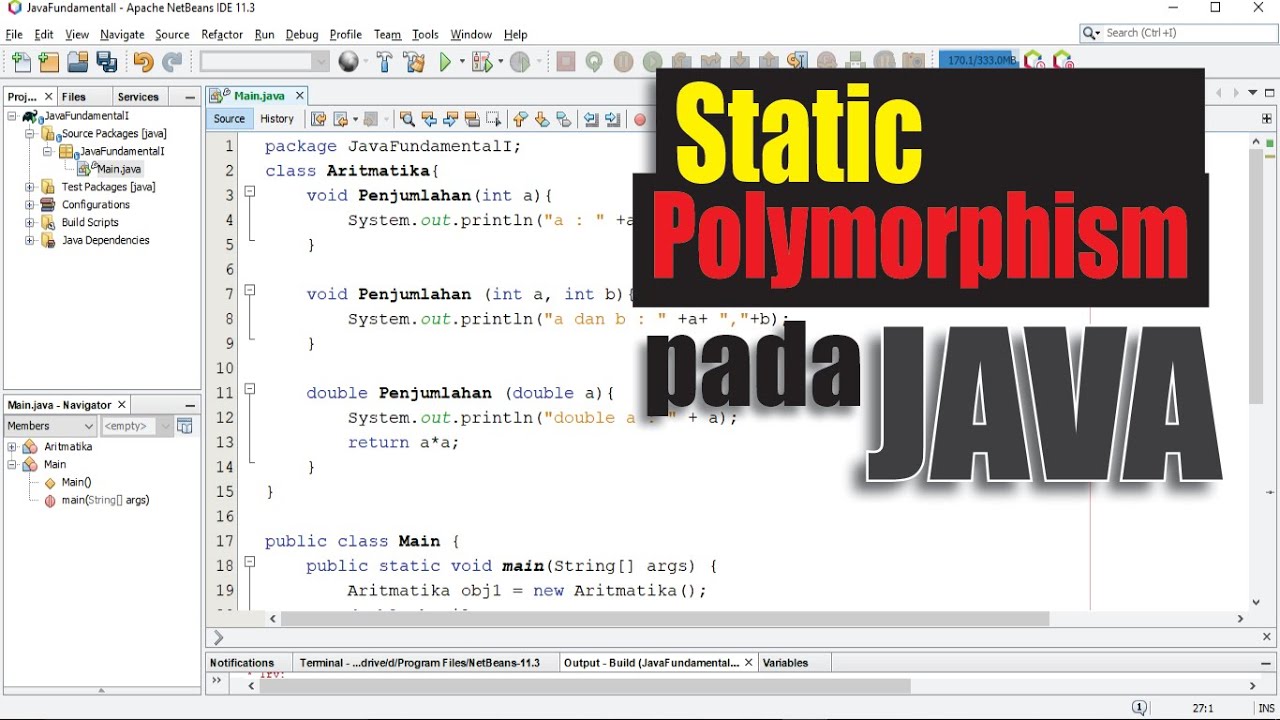
This article is a attempt to explore the concept with a focus on Java with appropriate illustrations and examples. The term “polymorphic” means “having multiple forms.” Polymorphism in Java simplifies programming by providing a single interface overlaid with multiple meanings as it goes through the rigor of subclassing. Polymorphism in Java is closely associated with the principle of inheritance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
